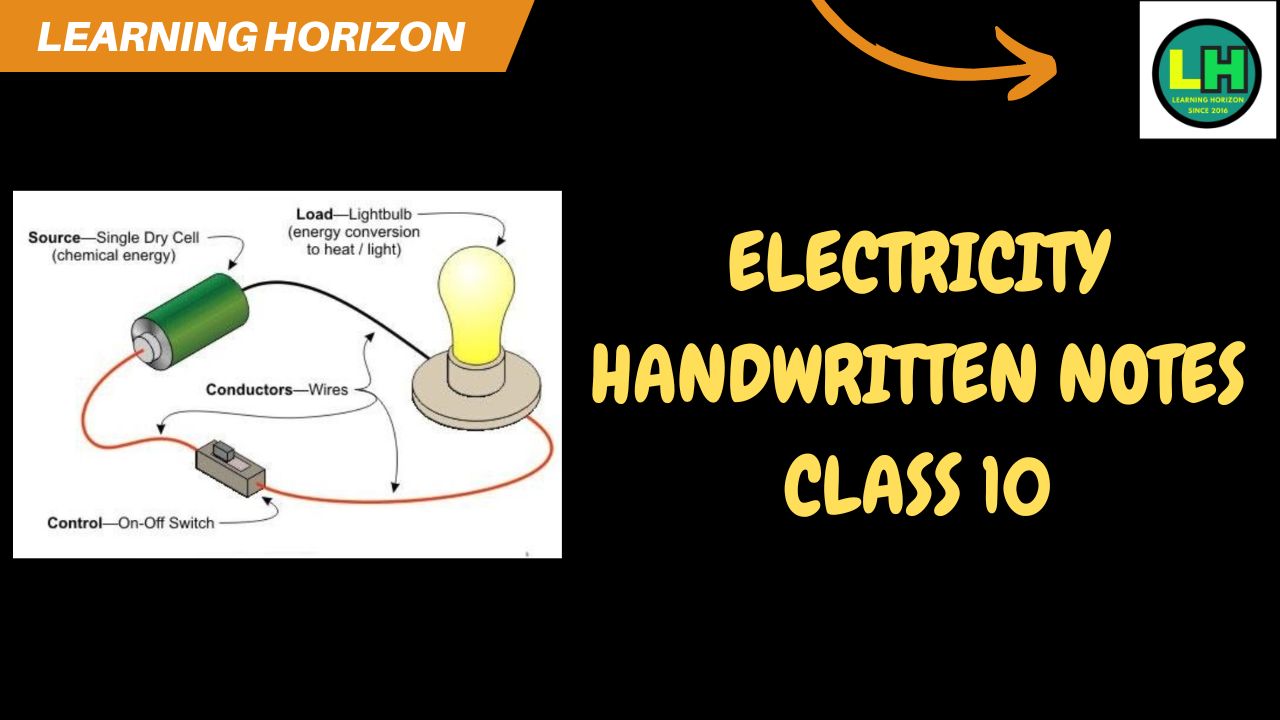
Electricity Handwritten Notes Class 10
Introduction
- Electricity is one of the most widely used forms of energy.
- It is caused by the flow of electric charges (usually electrons) through a conductor.
- The flow of charges constitutes electric current.
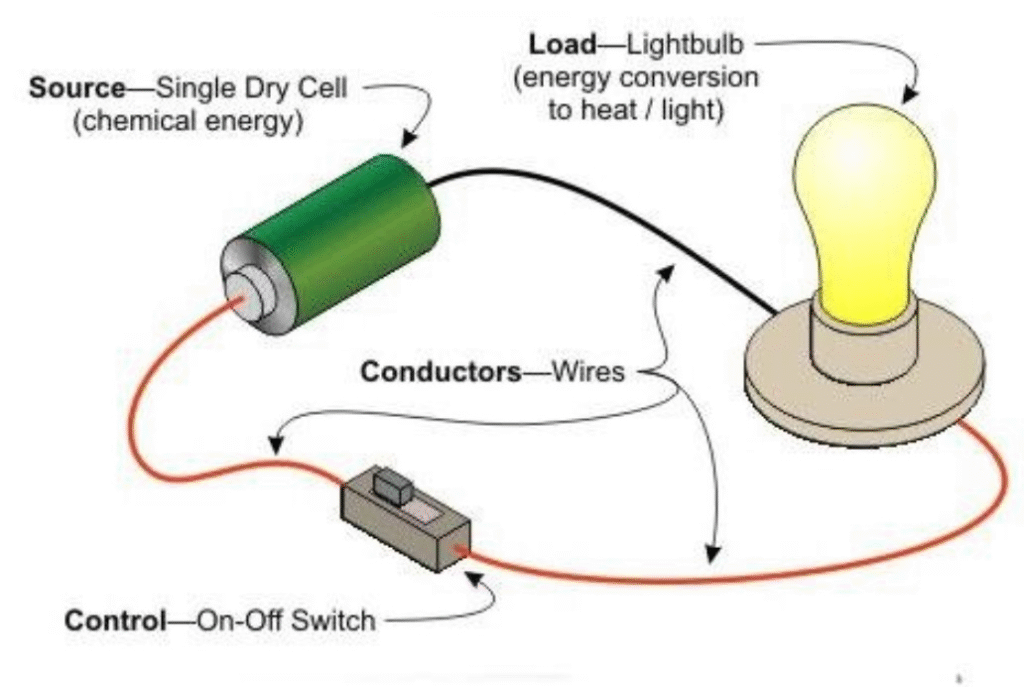
Electric Current (I)
- Definition: The rate of flow of electric charge through a conductor. I=Q/t
I → current (ampere, A)
Q → charge (coulomb, C)
t → time (second, s) - 1 Coulomb: Charge of 6.25×1018 electrons.
- 1 Ampere: Current when 1 coulomb of charge flows in 1 second.
- Current is measured by Ammeter
Electric Potential and Potential Difference (V)
- Electric Potential: The amount of work done in moving a unit charge from infinity to a point in an electric field.
- V=W/Q
- Potential Difference: Work done to move a unit charge between two points.
- Drives current in a circuit.
- Measured using Voltmeter (connected in parallel).
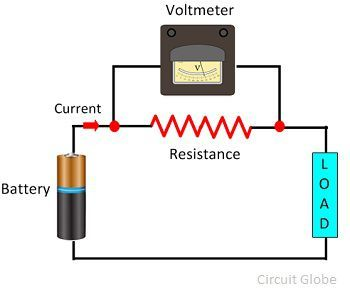
Unit: Volt (V)
1 Volt = 1 Joule / Coulomb
Electric Circuit
- Circuit: Closed path for current to flow.
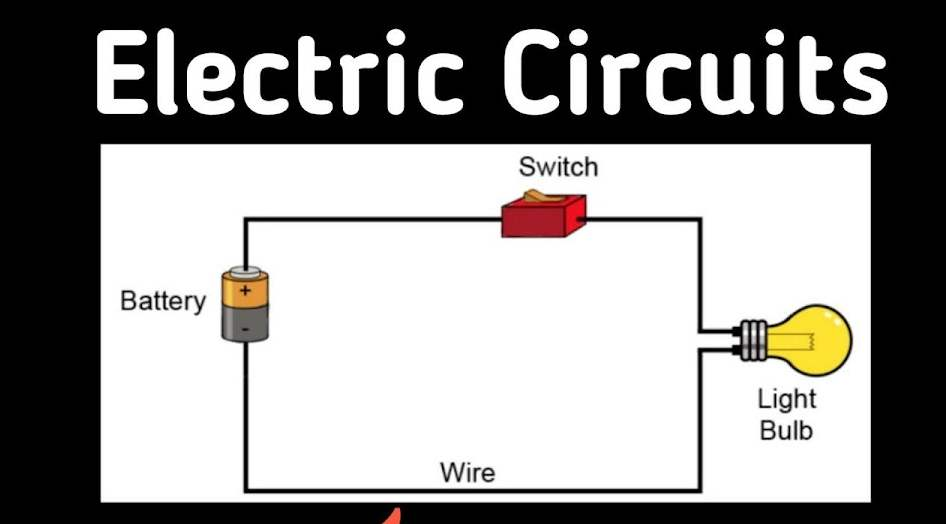
- Components:
- Cell/Battery
- Conducting wire
- Switch
- Bulb/Resistor
- Ammeter & Voltmeter
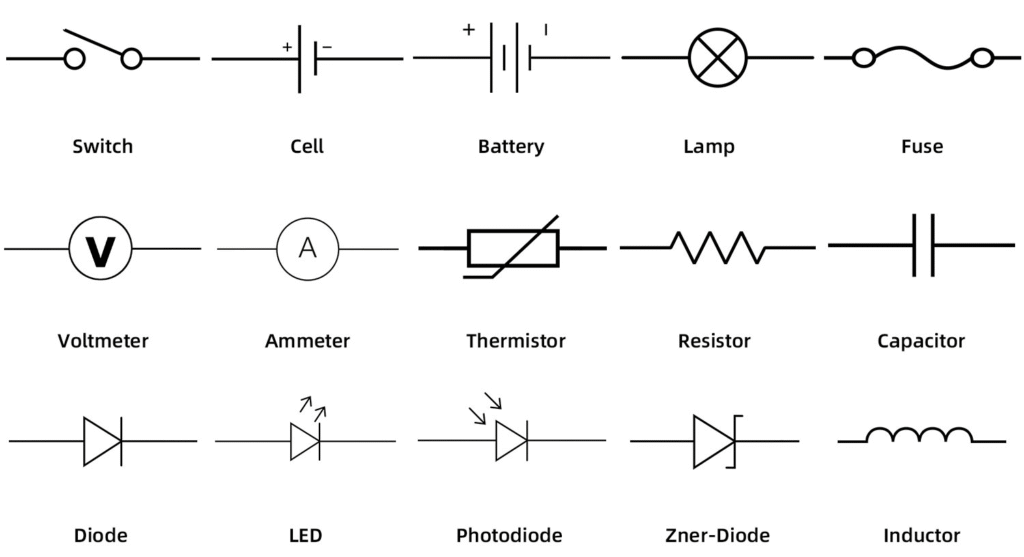
Conventions:
- Current flows from positive → negative terminal of battery (conventional current).
- Electrons move from negative → positive terminal.
Ohm’s Law
- Statement: At constant temperature, the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it. V∝I
- ⇒V=IR
- R = Resistance (ohm, Ω)
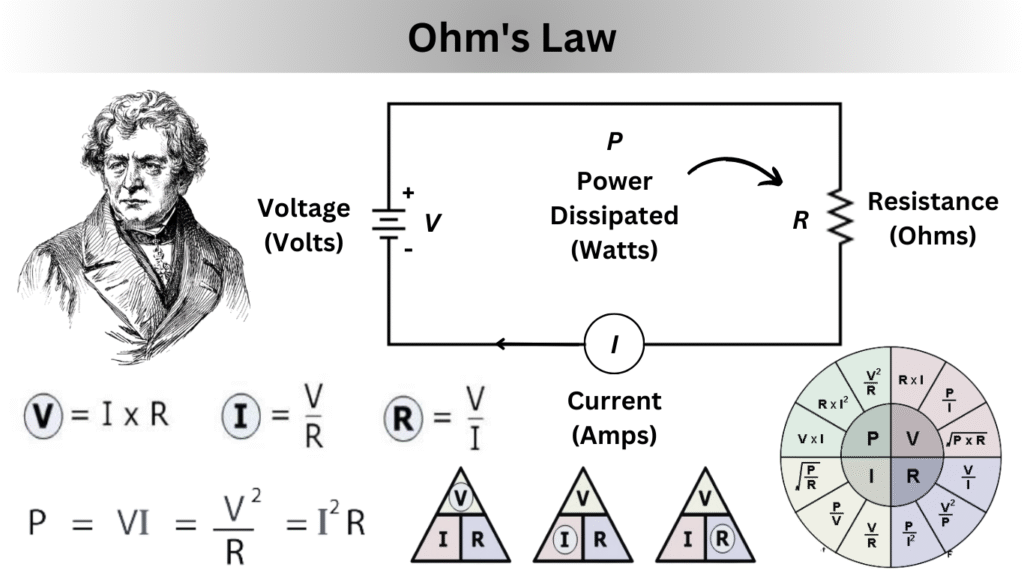
Graph:
- V–I graph is a straight line passing through the origin for ohmic conductors (like metals).
Read Also : Light chapter hand written notes
Resistance (R)
- Definition: Opposition offered by a conductor to the flow of electric current.
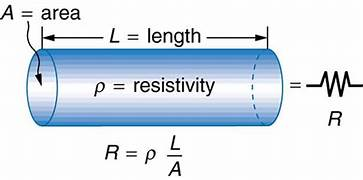
Formula: R=ρl/A
where,
ρ\rho → resistivity (Ωm)
l→ length of conductor
A→ cross-sectional area
Factors Affecting Resistance:
- Length (l): R∝l
- Area (A): R∝1/A
- Material: Different materials have different resistivity.
- Temperature: Resistance increases with temperature in metals.
Resistivity (ρ)
- Property of a material to resist current flow.
- Depends only on the nature of the material.
Unit: Ωm (ohm meter)
Good Conductors: Low resistivity (e.g., Copper, Silver)
Insulators: High resistivity (e.g., Rubber, Glass)
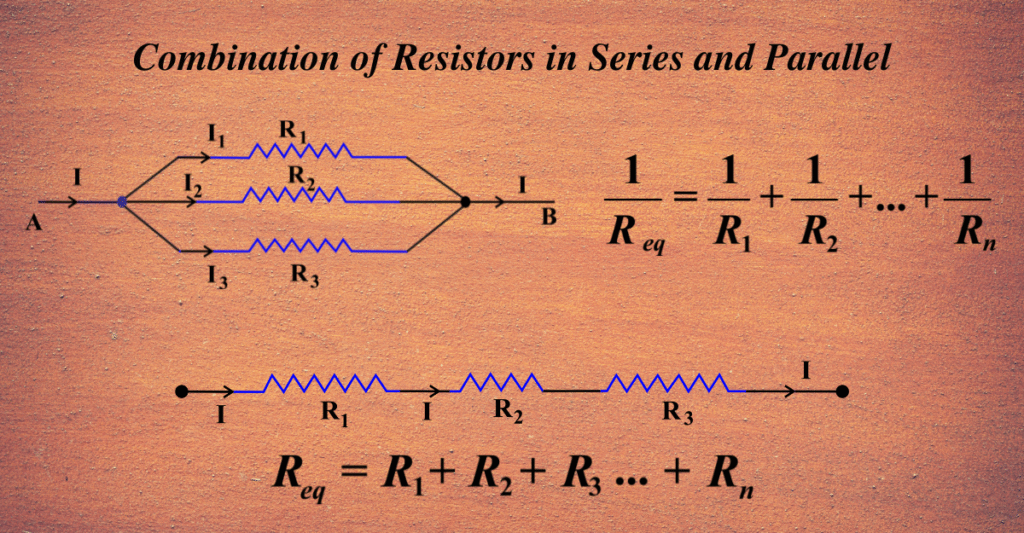
Combination of Resistors
(A) Series Combination
Rs=R1+R2+R3+…
- Current remains same.
- Potential difference divides.
(B) Parallel Combination
1
1/Rp=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3
- Voltage remains same.
- Current divides.
Electricity Handwritten best notes : Class 10
Heating Effect of Electric Current
When current passes through a conductor, heat is produced due to resistance.
Joule’s Law of Heating: H=I2Rt
where,
H → Heat produced (Joule)
I→ Current (Ampere)
R→ Resistance (Ohm)
t → Time (seconds)
Applications:
- Electric heater
- Electric iron
- Bulb filament
- Electric fuse
Electric Power (P)
- Rate of doing work or rate of consumption of electrical energy.
P=VI=I2R=V2/R
Unit: Watt (W)
1 Kilowatt (kW) = 1000 W
1 Unit of electricity = 1 kWh = 3.6 × 10⁶ J
Electric Fuse
- Safety device that prevents damage from excessive current.
- Fuse wire: high resistivity and low melting point (e.g., tin-lead alloy).
- Melts when current exceeds safe limit, breaking the circuit.
Household Circuits (Overview)
- Electric meter: Measures energy consumed (in kWh).
- Main switch: Controls power supply.
- Fuse/MCB: Safety device.
- Parallel connection: Used in homes so that each device works independently.
Important SI Units
| Quantity | Symbol | Unit | Instrument |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charge | Q | Coulomb (C) | — |
| Current | I | Ampere (A) | Ammeter |
| Potential Difference | V | Volt (V) | Voltmeter |
| Resistance | R | Ohm (Ω) | Ohmmeter |
| Power | P | Watt (W) | Wattmeter |
| Energy | E | Joule (J) | — |
Important Formulas Summary
| Concept | Formula |
|---|---|
| Current | I=Q/t |
| Potential Difference | V=W/Q |
| Ohm’s Law | V=IR |
| Resistance | R=ρl/A |
| Power | P=VI=I2R=V2/R |
| Energy | E=P×t |
| Heat Produced | H=I2Rt |
Electricity Handwritten Notes Class 10 | Easy & Complete Chapter Summary