Top Case Study Questions in Physics Class 12 | With Answer Key
1. Case Study: Optical Fibres in Modern Communication
Optical fibres are thin strands of glass or plastic that transmit light signals over long distances. The working principle of an optical fibre is Total Internal Reflection (TIR). When light enters one end of the fibre at a certain angle, it reflects internally along the fibre without escaping, provided the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
Optical fibres consist of three parts: core, cladding, and protective coating. The core has a higher refractive index than the cladding. This difference ensures that light undergoes TIR.
These fibres are widely used in telecommunication, internet transmission, medical endoscopy, and networking systems. They offer advantages like high bandwidth, low signal loss, and immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Questions:
Q1. What physical principle is responsible for the operation of an optical fibre?
Q2. Why should the refractive index of the core be higher than that of the cladding?
Q3. What condition must be satisfied for Total Internal Reflection to occur?
Q4. Mention any two advantages of using optical fibres over conventional wires.
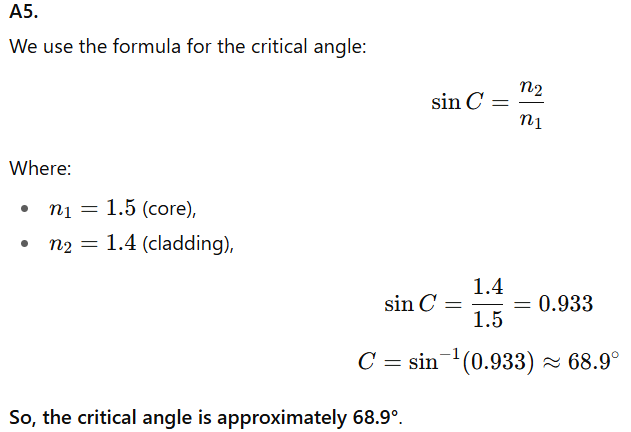
Q5. If the refractive index of the core is 1.5 and that of cladding is 1.4, calculate the critical angle for the fibre.
Answers:
A1. The working of optical fibres is based on the principle of Total Internal Reflection.
A2. The core must have a higher refractive index than the cladding to ensure that light reflects internally and doesn’t escape, thus enabling TIR.
A3. Two conditions must be satisfied for TIR:
- Light must travel from a denser to a rarer medium (higher to lower refractive index).
- The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
A4. Two advantages of optical fibres:
- High bandwidth and faster data transmission.
- Immunity to electromagnetic interference, leading to better signal quality.

Top Case Study Questions in Physics Class 12 | With Answer Key
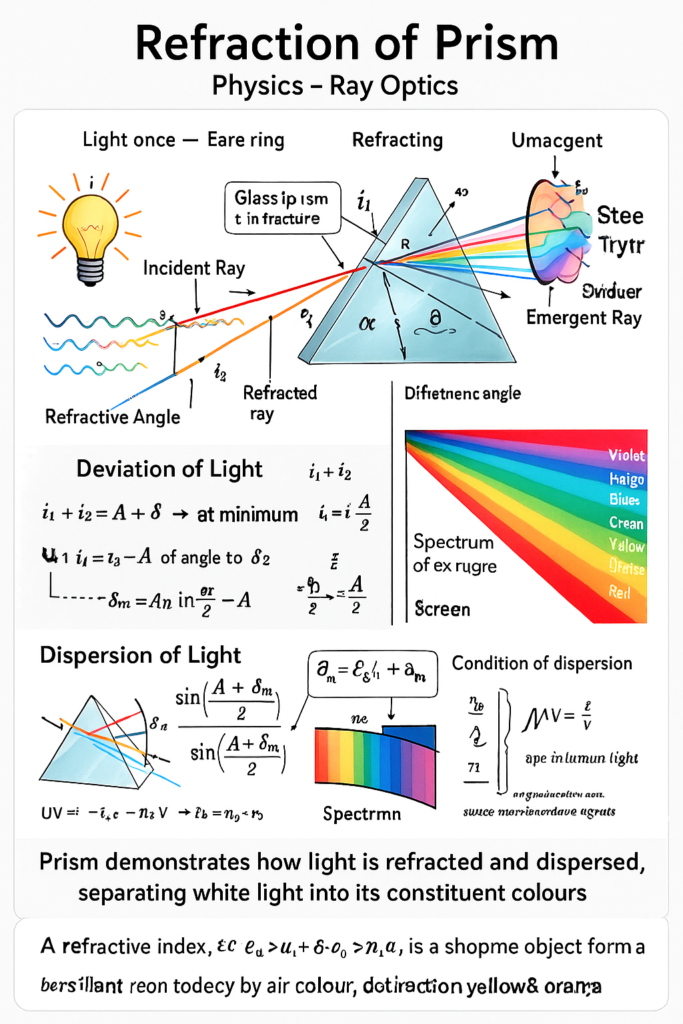
2.Case Study: Refraction Through a Prism
A glass prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. When a ray of light enters a prism, it bends towards the base, gets refracted again as it exits, and emerges in a new direction. This deviation of light depends on the angle of incidence, refractive index, and the angle of the prism.
For a prism of small angle AAA, the angle of deviation δ\deltaδ is minimum when the light passes symmetrically through the prism. This condition is known as the condition for minimum deviation.
The formula relating the refractive index (n) of the prism material to the angle of prism (A) and angle of minimum deviation (D) is:
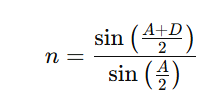
Prisms are widely used in spectrometers, binoculars, and optical instruments due to their ability to disperse white light into its constituent colors (dispersion).
Answers:
A1. The condition for minimum deviation occurs when the incident and emergent rays make equal angles with the prism’s faces, i.e., the light passes symmetrically through the prism.
A2. The prism deviates light towards its base because of the difference in the refractive index of the prism material and air. The light bends towards the base upon entering and exiting the prism.
A3. The formula is:
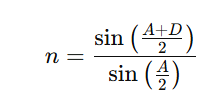
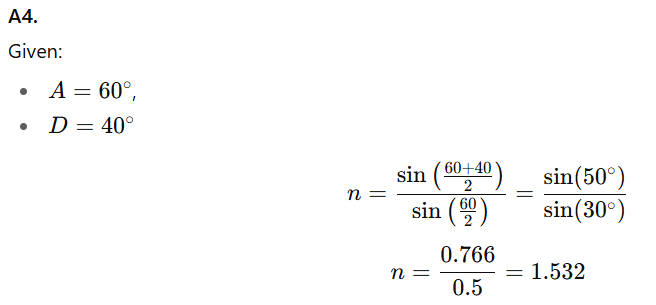
A5. Prisms are used in spectrometers to measure the wavelength of light or analyze light spectra.

3. Case Study: Magnetic Effects of Moving Charges
When a charge moves, it creates a magnetic field. This is the basis of electromagnetism. The strength and direction of the magnetic field due to a moving charge or current-carrying conductor are determined by Biot–Savart Law and Ampere’s Circuital Law.

Questions:
Q1. What is the direction of the magnetic force on a positively charged particle moving perpendicular to a magnetic field?
A. Along velocity
B. Opposite to velocity
C. Perpendicular to both velocity and magnetic field
D. Parallel to the magnetic field
Q2. The force on a moving charge in a magnetic field is zero when:
A. Charge is zero
B. Velocity is zero
C. Velocity is parallel or antiparallel to the magnetic field
D. All of the above
Q3. A proton enters a magnetic field of 0.2 T at a speed of 106 m/s perpendicular to the field. Calculate the radius of its circular path.
(Mass of proton =1.67×10−27kg, charge q=1.6×10−19 C
Q4. State the Biot–Savart Law in vector form.
Q5. Name one device that works on the principle of the magnetic force on a moving charge.
Answers:
A1. C. Perpendicular to both velocity and magnetic field
A2. D. All of the above
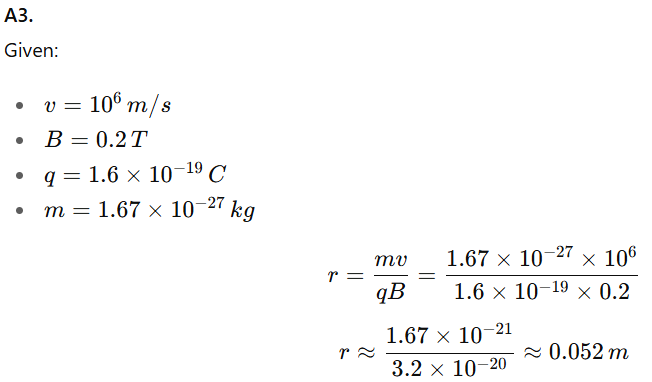

A5. Cyclotron, Mass Spectrometer, or CRT (Cathode Ray Tube)

Top Case Study Questions in Physics Class 12 | With Answer Key
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
A transformer is a device used to change the alternating voltage using the principle of mutual induction. It consists of two coils — the primary and secondary — wound on the same iron core. If the secondary coil has more turns than the primary, the voltage is increased, and the transformer is called a step-up transformer. If the secondary coil has fewer turns, it decreases the voltage and is called a step-down transformer.
In practical use, transformers are highly efficient but not ideal. Some power is lost in the form of heat due to resistance of windings, eddy currents, hysteresis in the core, and leakage of magnetic flux. Despite these, they play a vital role in transmitting electricity at high voltages over long distances, reducing the loss of power.
Questions:
Q1. Which principle is used in the working of a transformer?
a) Self-induction
b) Mutual induction
c) Electromagnetic force
d) Ohm’s
Answer: (b) Mutual induction
A transformer works because a changing current in the primary coil induces an emf in the secondary coil through the mutual induction principle.
Q2. A transformer has 500 turns in the primary coil and 5000 turns in the secondary coil. If the input voltage is 220 V, the output voltage will be:
a) 22 V
b) 220 V
c) 2200 V
d) 110 V
Answer: (c) 2200 V
Formula:
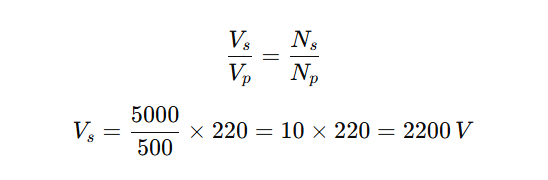
Q3. What type of transformer is used in the main power station to transmit electricity over long distances?
a) Step-down
b) Step-up
c) Auto-transformer
d) None of these
Answer: (b) Step-up
At power stations, voltage is increased (stepped up) to reduce current and hence minimize power loss during transmission.
Q4. Mention any two causes of energy loss in a transformer.
Answer:
- Heat loss due to resistance of winding (I²R loss).
- Eddy current loss in the iron core.
(Other possible answers: hysteresis loss, leakage of magnetic flux.)
Q5. A step-down transformer is used with a doorbell that requires 12 V. If the primary coil has 1000 turns and the secondary coil has 100 turns, what should be the input voltage?
Answer:
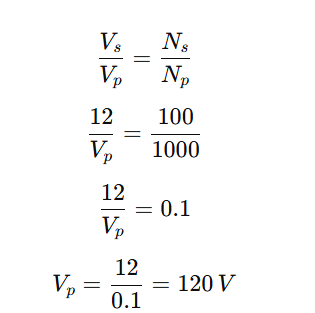
Top Case Study Questions in Physics Class 12 | With Answer Key
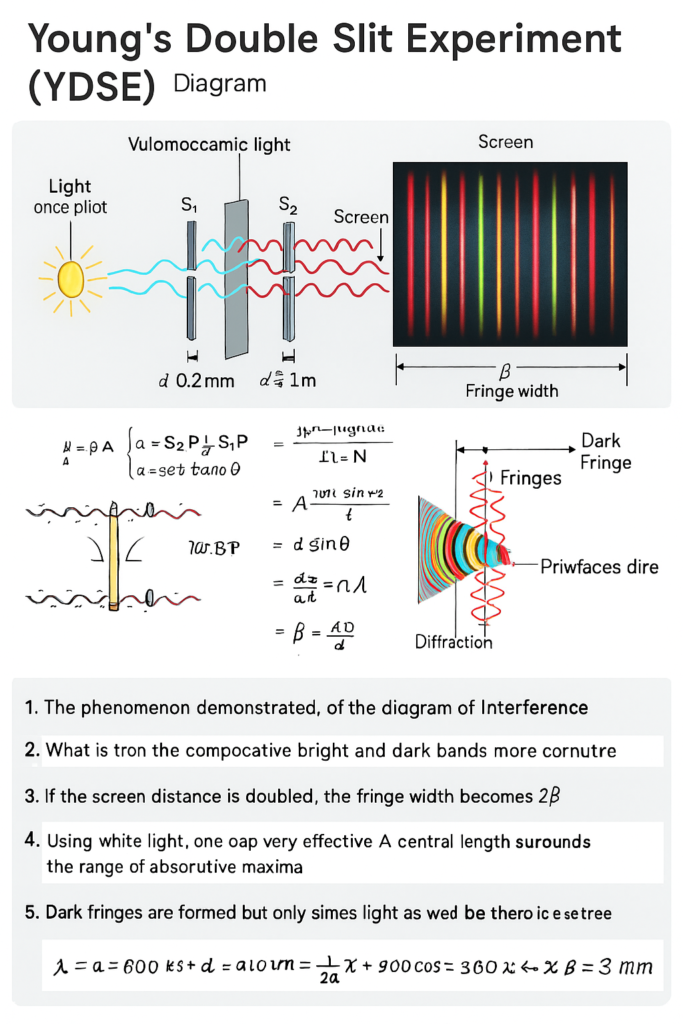
answers:
1. The phenomenon demonstrated, of the diagram of Interference
→ Interference of light (constructive and destructive).
2. What is from the compocative (comparative) bright and dark bands more contrust?
→ If the light is monochromatic and coherent, the contrast between bright and dark bands is sharp.
3.If the screen distance is doubled, the fringe width becomes 2β
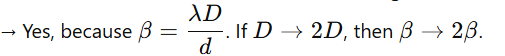
4. Using white light, one can observe a central bright white fringe surrounded by colored fringes
→ The central fringe is white, while the side fringes are colored and overlapping.
5.Dark fringes are formed but only some light as well as theoretical