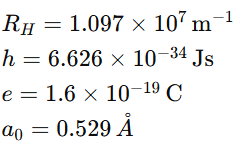Atoms Class 12 Notes PDF Download
Chapter: Atoms – Class 12 Physics Notes

1. Introduction
- The concept of atom originated from Greek philosophers like Democritus and Dalton’s atomic theory.
- Modern atomic models are based on experimental studies on atomic structure, spectra, and radiation.
2. Rutherford’s Nuclear Model of Atom
Experiment: Alpha particle scattering experiment by Geiger and Marsden under Rutherford’s supervision.
Observations:
- Most α-particles passed undeviated → Most of atom is empty space.
- Few were deflected → Existence of a dense positive center (nucleus).
- Very few bounced back → Nucleus is very small and massive.
Conclusions:
- Atom consists of a positively charged nucleus at center.
- Electrons revolve around nucleus in circular orbits.
- Electrostatic force provides centripetal force.
Drawbacks:
- Could not explain stability of atom.
- Could not explain discrete line spectra of elements.
Atoms Class 12 Notes PDF Download | Quick Revision & Important Concepts
3. Atomic Spectra
- Each element emits/absorbs light of definite wavelengths → line spectrum.
- Hydrogen spectrum has series of lines corresponding to transitions between energy levels.
Spectral Series of Hydrogen:
| Series | Region | Transition (n₂ → n₁) |
|---|---|---|
| Lyman | Ultraviolet | n₂ → 1 |
| Balmer | Visible | n₂ → 2 |
| Paschen | Infrared | n₂ → 3 |
| Brackett | Infrared | n₂ → 4 |
| Pfund | Infrared | n₂ → 5 |
Wavelength formula (Rydberg formula):
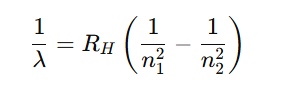
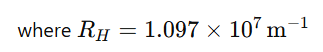
4. Bohr’s Model of Atom
Postulates:
- Electron revolves around nucleus in certain discrete orbits (stationary states) without radiating energy.
- Angular momentum quantized: mvr=nh/2π, n=1,2,3,…
- Energy is emitted or absorbed only when electron jumps between orbits: ΔE=E2−E1=hν
Energy of nth orbit: En=−13.6/n2 eV
Radius of nth orbit: rn=n2a0, a0=0.529 A˚
Velocity: vn=2.18×106n m/s
5. Energy Level Diagram
- Negative sign of energy shows electron is bound to nucleus.
- Energy levels converge as nnn increases.
- Ionization energy of hydrogen = 13.6 eV (energy required to remove electron from n = 1 to ∞).
6. Limitations of Bohr’s Model
- Could not explain fine structure of spectral lines.
- Failed for multi-electron atoms.
- Violated uncertainty principle.
- Could not explain Zeeman and Stark effects.
7. Important Formulas
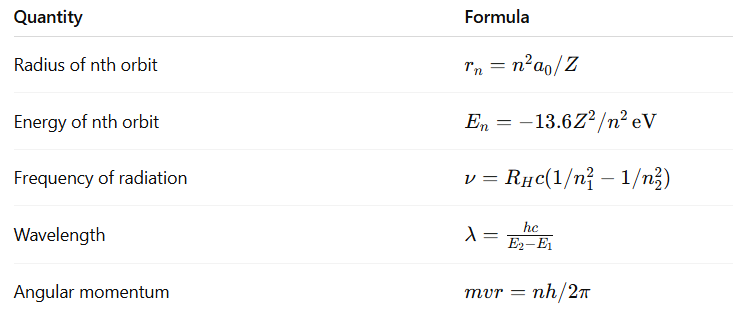
8. Key Points to Remember
- n=1 → Ground state
- n>1 → Excited states
- Absorption → Electron jumps to higher orbit
- Emission → Electron falls to lower orbit
- Ionization potential of H=13.6 V
→ Red line of Balmer series.
9. Important Constants