Class 10 Light Handwritten Notes PDF | Diagrams & Key Concepts
Light and Reflection of Light
Light is a form of energy that enables us to see the world around us. It travels in straight lines in the form of waves and can exhibit properties of both waves and particles. One of the fundamental behaviors of light is reflection, in which light rays bounce back when they strike a smooth and shiny surface, such as a mirror. Reflection follows two basic laws:
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in the same plane.
Reflection is classified into regular reflection (from smooth surfaces) and diffused reflection (from rough surfaces). This concept forms the basis for devices like mirrors, periscopes, and optical instruments.
1. Ray & Beam of Light
- Ray: A straight path along which light energy travels.
- Beam: A collection of light rays. Types include parallel, divergent, and convergent beams.
2. Reflection of Light
- Occurs when light bounces off a surface.
- Laws of Reflection:
- The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal lie in the same plane.
- Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection (∠i = ∠r).
3. Image Formation
- Real Image: Formed by actual convergence of light rays.
- Virtual Image: Formed by apparent convergence of reflected rays.
4. Spherical Mirrors (Concave & Convex)
- Concave: Curves inward; converges light to a focus.
- Convex: Curves outward; diverges light, offering a wider field of view.
5. Mirror Formula & Magnification
- Mirror formula (for spherical mirrors): Relates object distance (u), image distance (v), and focal length (f).
- Magnification (m): Ratio of image height to object height; sign indicates nature (real or virtual).
6. Refraction of Light
- The bending of light as it passes between different media.
- Laws of Refraction:
- Incident ray, refracted ray, and the normal are coplanar.
- Ratio of sine of incidence angle to sine of refraction angle is constant (Snell’s Law).
- Refractive Index (n₁₂): Ratio of light speed in medium 1 to that in medium 2.
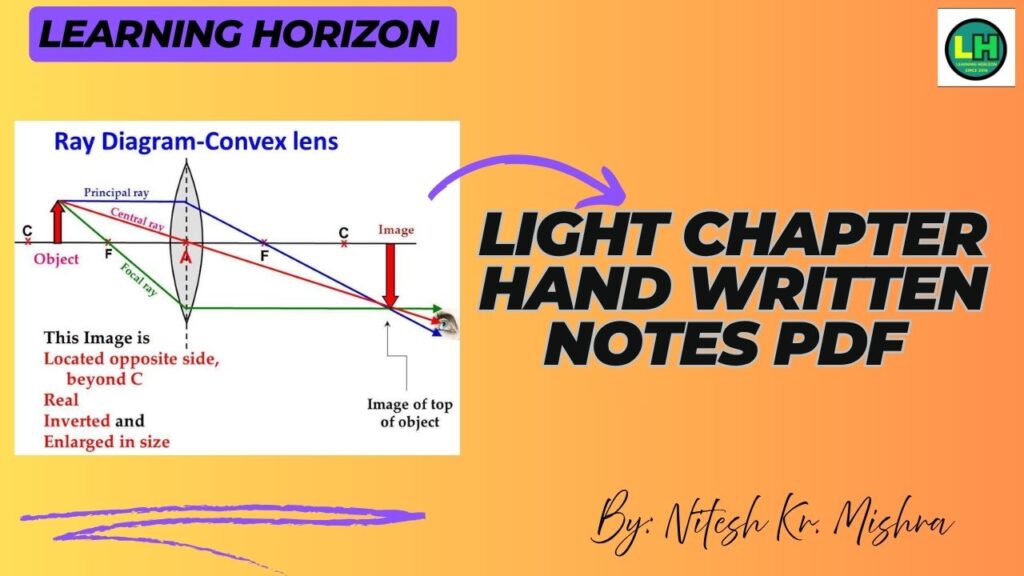
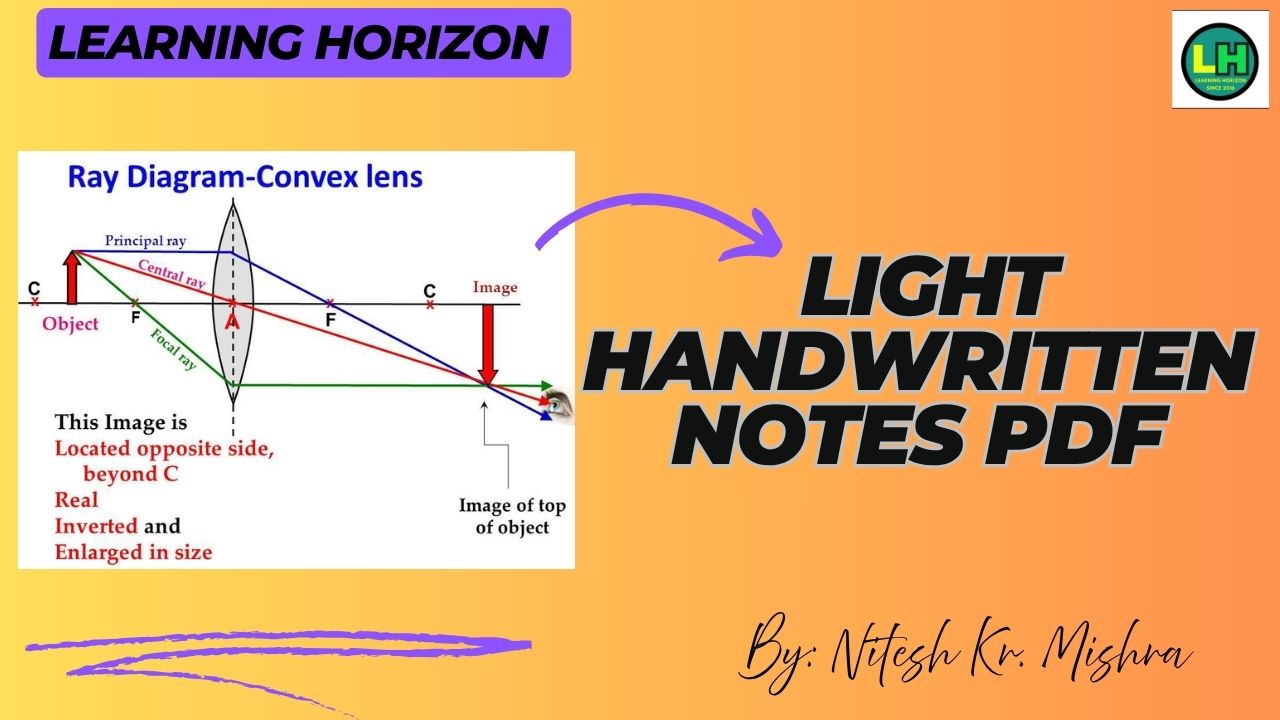
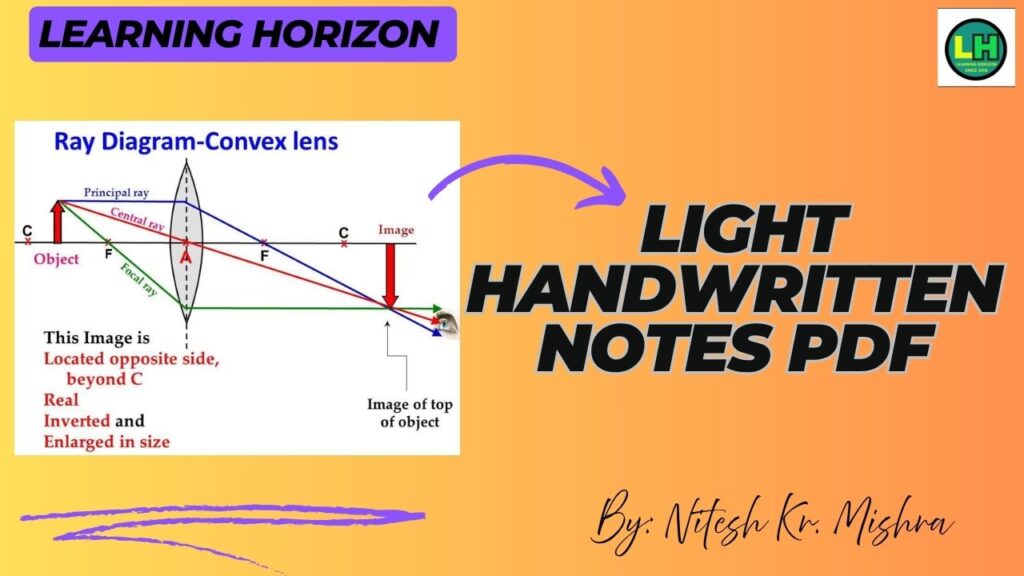
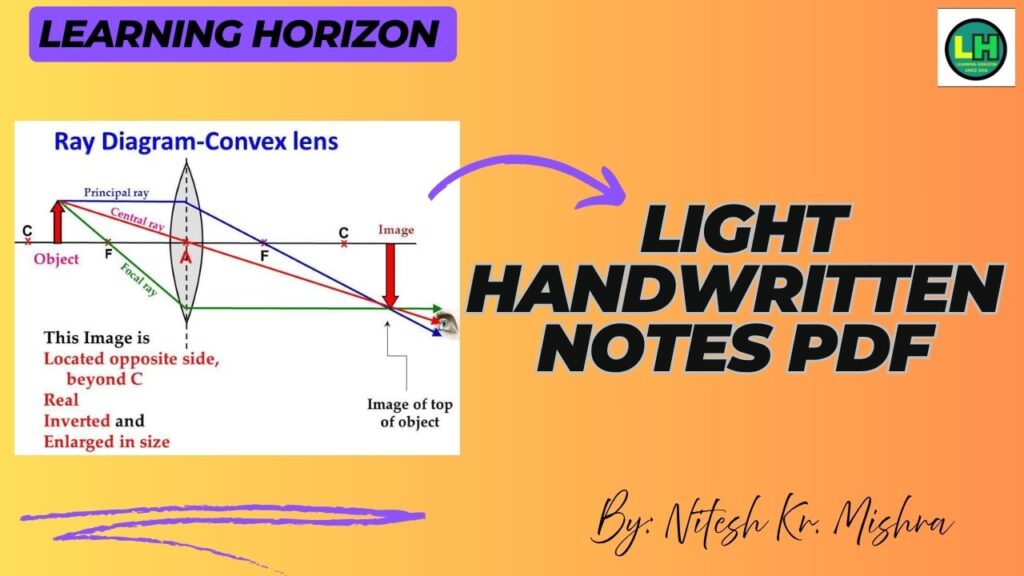
7. Lenses (Convex & Concave)
- Convex Lens: Thicker in the center, converges rays.
- Concave Lens: Thicker at edges, diverges rays.
- Important terms include optical centre, principal axis, and principal focus.
8. Lens Formula & Power
- Lens formula: Connects object distance, image distance, and focal length.
- Power: Ability of a lens to converge/diverge light; measured in dioptres (D). For combinations, total power = sum of individual powers.
Light chapter hand written notes pdf