Tissues Class 9 Science Notes PDF
Tissues Class 9 Science Notes
Download the best Tissues Class 9 Science Notes PDF for quick and easy revision. These notes are based on the latest NCERT curriculum and cover all key topics from Chapter 6 – Tissues including:
- Plant tissues: Meristematic and Permanent tissues
- Simple permanent tissues: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
- Complex permanent tissues: Xylem and Phloem
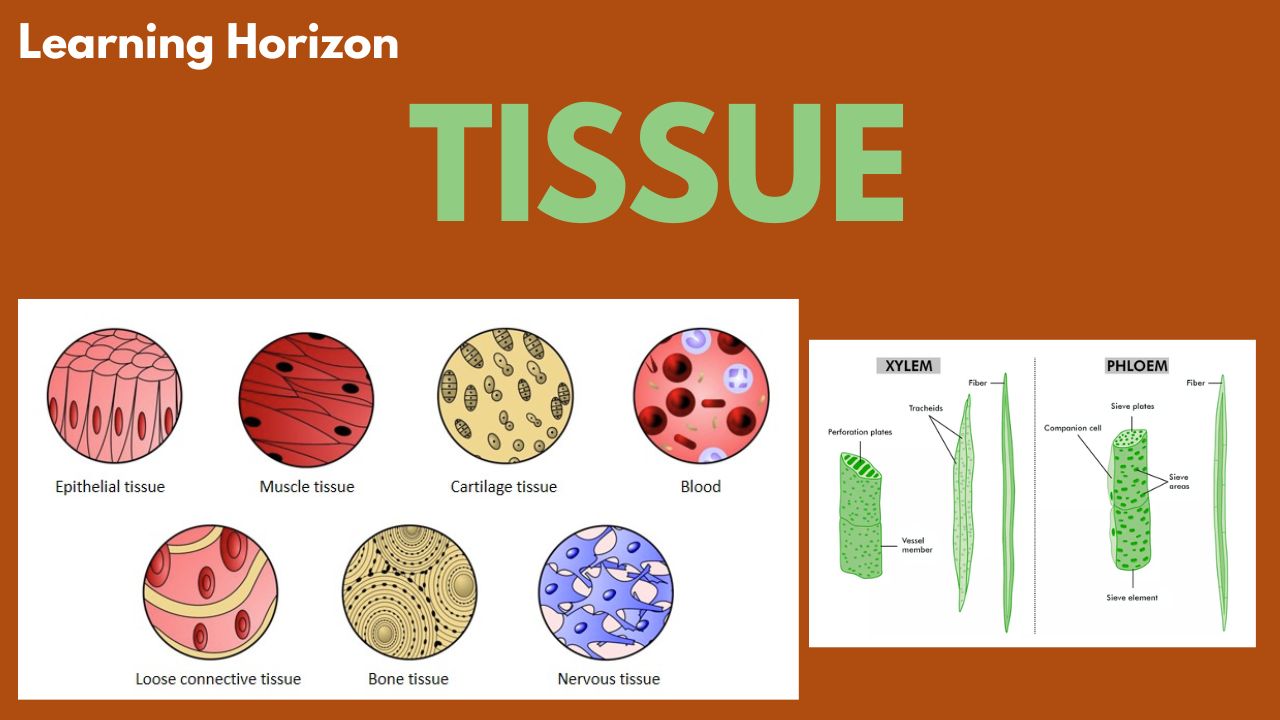
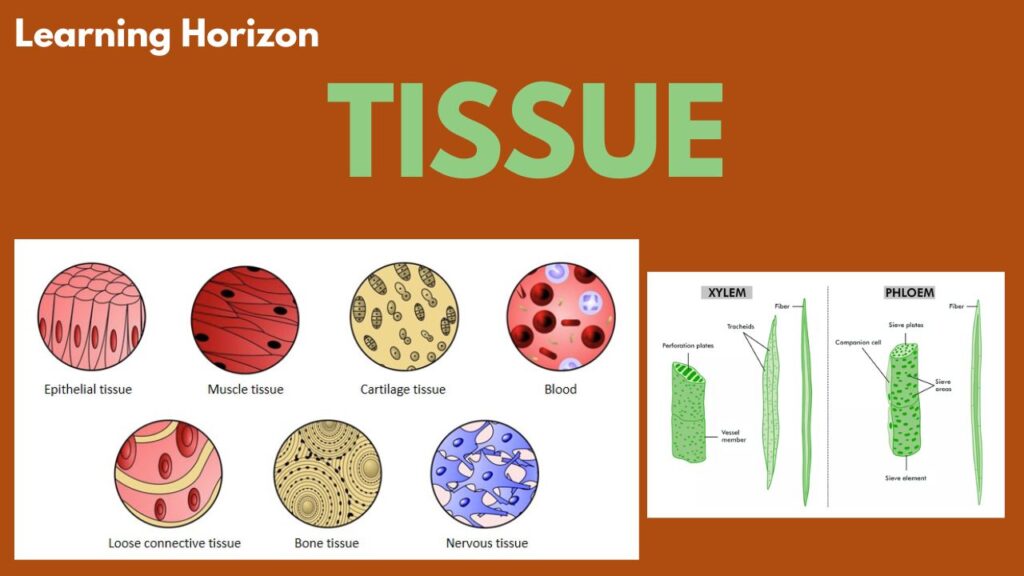
- Animal tissues: Epithelial, Muscular, Connective, and Nervous tissues
- Labeled diagrams, definitions, and example
Plant tissues: Meristematic and Permanent tissues
1. Meristematic Tissues
Meristematic tissues are groups of actively dividing cells found in specific regions of the plant.
➤ Characteristics:
- Cells are small, with a dense cytoplasm.
- Nucleus is large; vacuoles are either small or absent.
- Cell walls are thin and made of cellulose.
- Found in growing regions of plants.
➤ Types of Meristematic Tissues:
- Apical Meristem:
- Found at the tips of roots and shoots.
- Responsible for the increase in length of the plant (primary growth).
- Intercalary Meristem:
- Located at internodes or base of leaves (in grasses).
- Helps in the regrowth of parts.
- Lateral Meristem (Cambium):
- Found on the sides of stems and roots.
- Responsible for the increase in girth (secondary growth).
🔹 2. Permanent Tissues
Permanent tissues are formed from meristematic tissues once they lose their ability to divide.
➤ Types of Permanent Tissues:
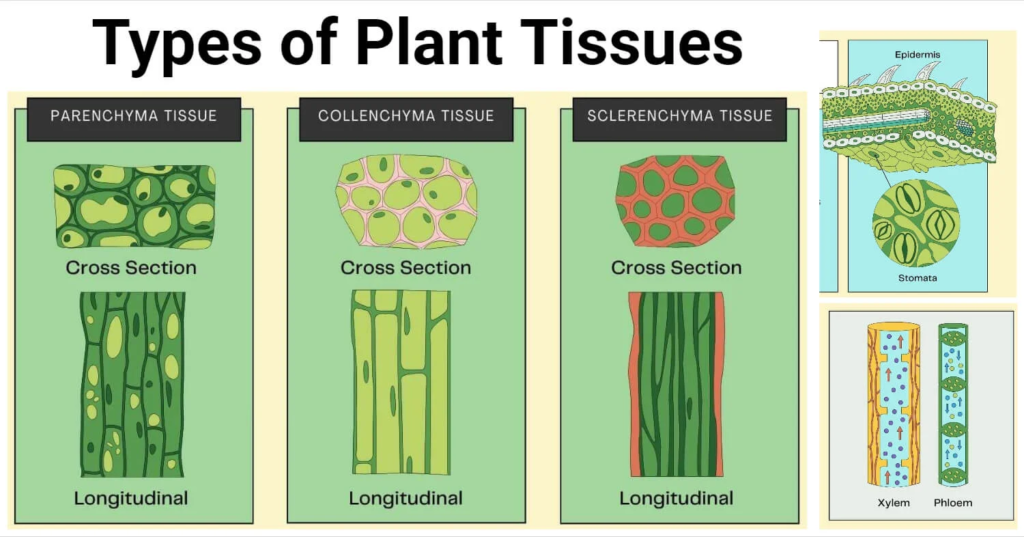
A. Simple Permanent Tissues – Made up of similar types of cells.
- Parenchyma
- Soft, living cells with thin walls.
- Function: Storage, photosynthesis (if chlorophyll present – called chlorenchyma), and support.
- Example: Pith of stem.
- Collenchyma
- Living cells with thick corners due to cellulose and pectin.
- Function: Provides flexibility and mechanical support.
- Found in leaf stalks and stems.
- Sclerenchyma
- Dead cells with thick, lignified walls.
- Function: Gives strength and rigidity.
- Found in seed coats, husk of coconut.
B. Complex Permanent Tissues – Made up of different types of cells.
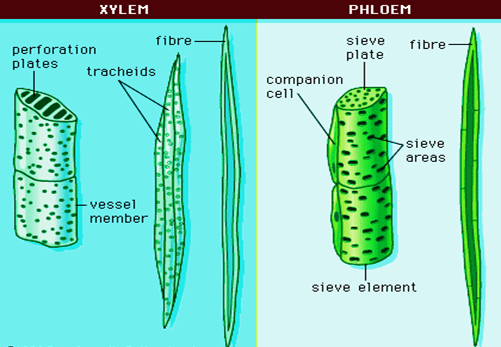
- Xylem (conducts water and minerals):
- Components: Tracheids, Vessels, Xylem parenchyma, Xylem fibres.
- Phloem (conducts food):
- Components: Sieve tubes, Companion cells, Phloem parenchyma, Phloem fibres.
- Tissues Class 9 Science Notes PDF | Chapter 6 with Diagrams
Animal tissue
1. Epithelial Tissue
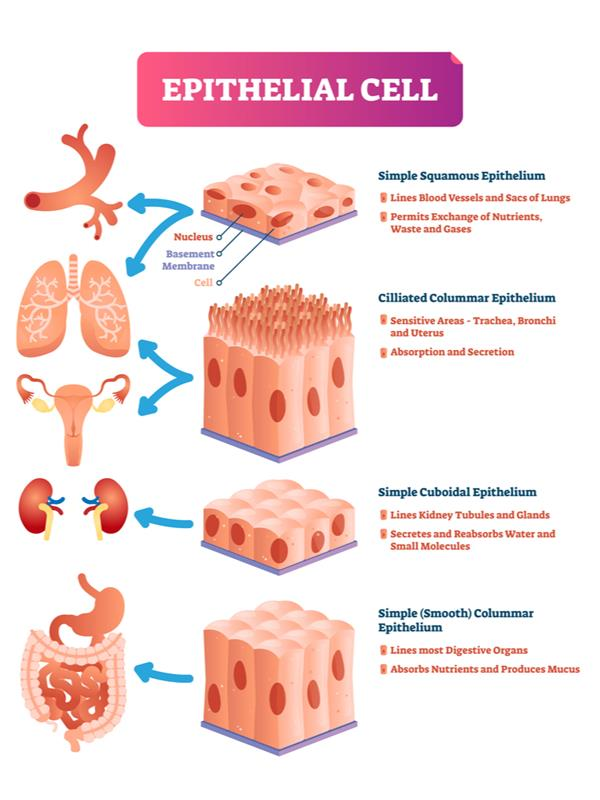
Covers the body surface and lines internal organs and cavities.
➤ Characteristics:
- Cells are tightly packed with very little intercellular space.
- Acts as a protective layer.
- Can be single-layered (simple) or multi-layered (stratified).
➤ Types of Epithelial Tissue:
- Squamous Epithelium – Thin and flat cells (e.g., lining of mouth, blood vessels).
- Cuboidal Epithelium – Cube-shaped cells (e.g., kidney tubules).
- Columnar Epithelium – Tall, pillar-like cells (e.g., lining of intestine).
- Ciliated Epithelium – Columnar cells with cilia (e.g., respiratory tract).
- Glandular Epithelium – Specialized for secretion (e.g., glands).
🔹 2. Connective Tissue
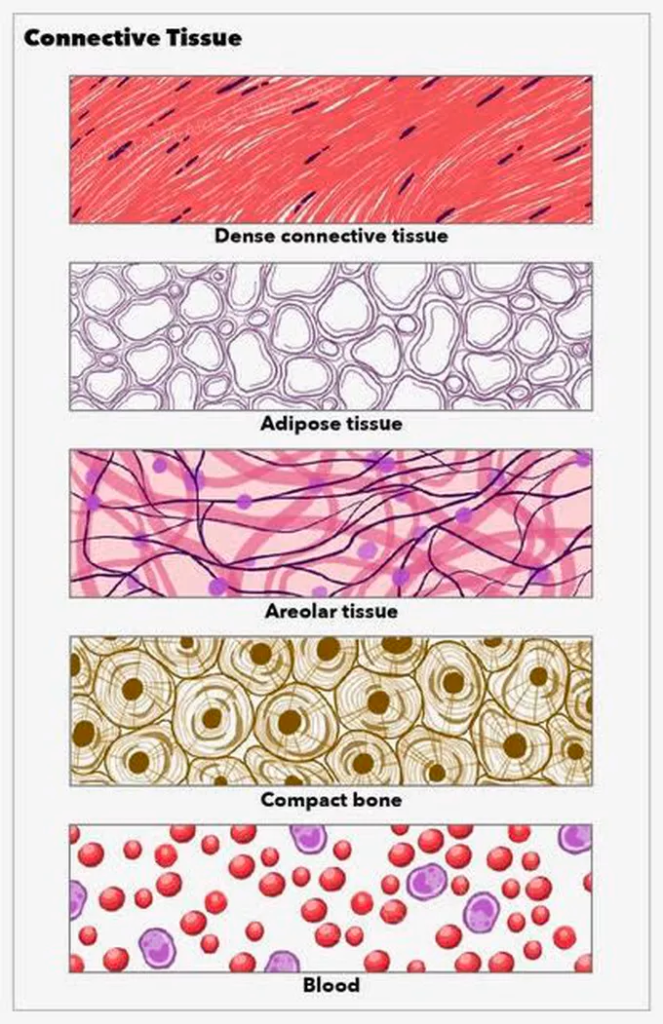
Connects and supports different parts of the body.
➤ Types of Connective Tissue:
- Areolar Tissue
- Found between skin and muscles.
- Function: Fills space inside organs, provides support.
- Adipose Tissue
- Fat-storing tissue beneath the skin.
- Function: Insulation and energy storage.
- Ligaments
- Connect bone to bone.
- Strong but elastic.
- Tendons
- Connect muscle to bone.
- Strong but less elastic.
- Cartilage
- Flexible tissue (e.g., ear, nose tip).
- No blood supply.
- Bone
- Hard and strong tissue with calcium and phosphorus.
- Supports and protects organs.
- Blood
- Fluid connective tissue.
- Transports gases, nutrients, hormones, etc.
🔹 3. Muscular Tissue
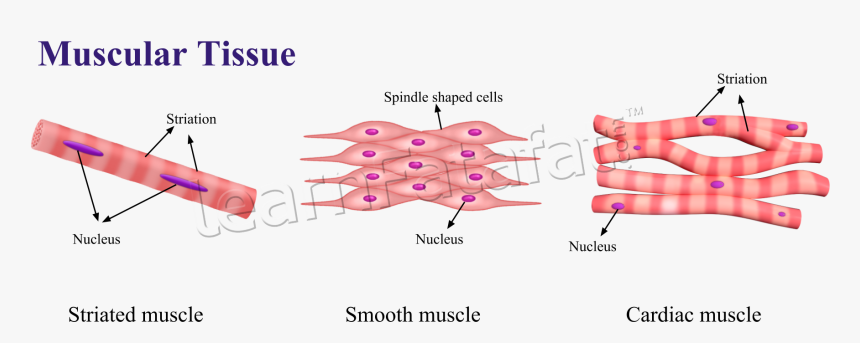
Helps in movement of body parts through contraction and relaxation.
➤ Types of Muscular Tissue:
- Striated (Skeletal) Muscles
- Voluntary, striped appearance.
- Attached to bones, used for body movement.
- Unstriated (Smooth) Muscles
- Involuntary, no striations.
- Found in internal organs like stomach, intestines.
- Cardiac Muscles
- Involuntary, striated, and branched.
- Found only in the heart.
🔹 4. Nervous Tissue
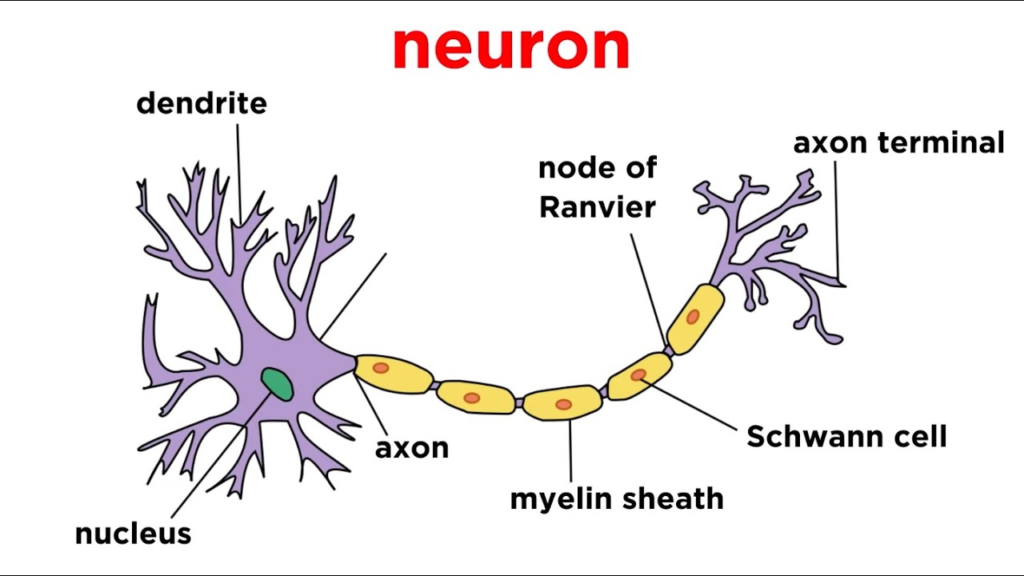
Specialized for transmitting messages in the form of electrical impulses.
➤ Main Cell: Neuron
- Structure: Cell body, axon, dendrites.
- Function: Carry messages between brain, spinal cord, and body.
Tissues Class 9 Science Notes PDF | Chapter 6 with Diagrams