
Case Study Objective:
The objective of this case study is to examine/analyze/evaluate [subject] in order to understand [specific aspect], identify [key issue/opportunity], and provide insights or solutions that can be applied to [context or future application].
Half Yearly Science case study 2025
Case Study: The Cell – Fundamental Unit of Life
All living organisms are made up of cells. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. Some organisms like Amoeba are made up of a single cell (unicellular), while others like humans are made up of many cells (multicellular).
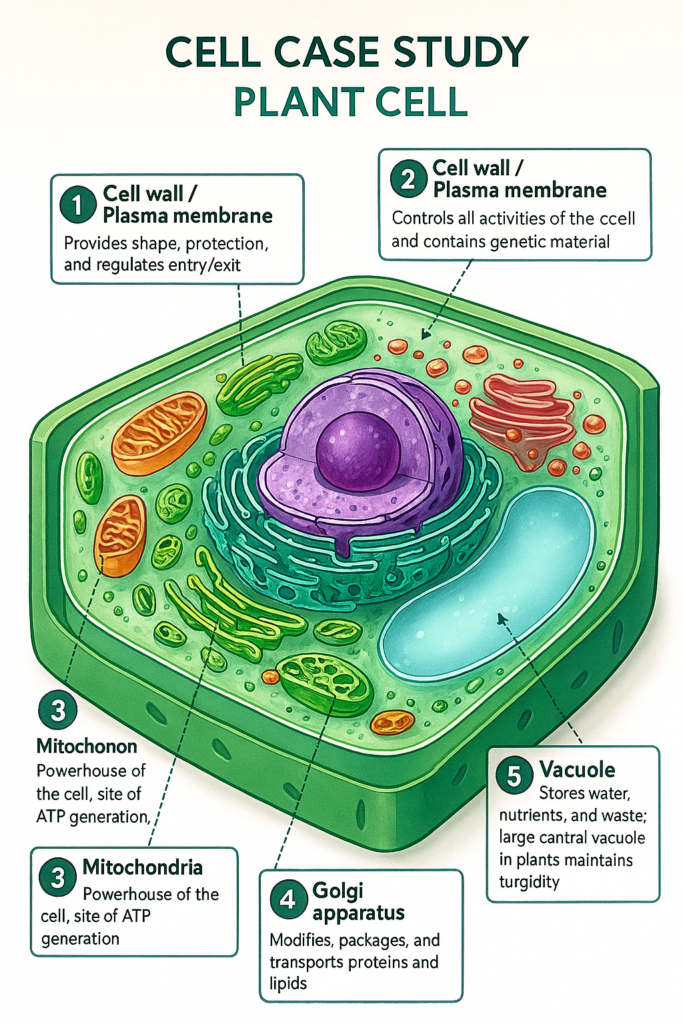
Cells have different shapes and sizes based on their function. Each cell has three main parts – the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. The plasma membrane controls the entry and exit of substances. The nucleus acts as the control center of the cell and contains genetic material. The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance where various organelles are found.
In plant cells, an additional cell wall is present which provides rigidity. Also, plant cells have large vacuoles and chloroplasts which are absent in animal cells. Different organelles like mitochondria (powerhouse of the cell), Golgi apparatus, and endoplasmic reticulum perform specific functions.
Understanding the structure and function of the cell helps us understand how living organisms survive, grow, and reproduce.
Questions:
Q1. What is the structural and functional unit of life?
Q2. Name the three main parts of a cell.
Q3. Which cell organelle is known as the ‘powerhouse of the cell’?
Q4. Give two differences between plant cells and animal cells.
Q5. What is the function of the plasma membrane?
Answers:
A1. The cell is the structural and functional unit of life.
A2. The three main parts of a cell are the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
A3. The mitochondrion is known as the ‘powerhouse of the cell’.
A4.
- Plant cells have a cell wall, while animal cells do not.
- Plant cells contain chloroplasts and have large vacuoles, while animal cells do not have chloroplasts and have small or no vacuoles.
A5. The plasma membrane controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell; it acts as a selectively permeable barrier.
Case Study Diagram : Tissue
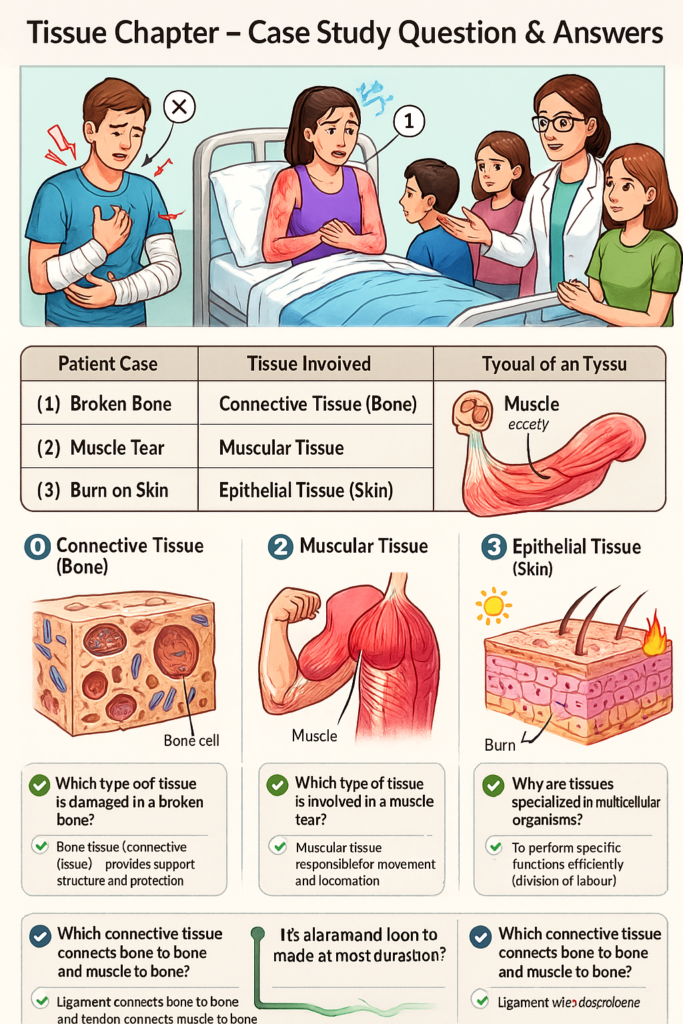
Question & Answers
Q1. Which type of tissue is damaged in a broken bone?
A: Bone tissue (connective tissue) – provides support, structure, and protection.
Q2. Which type of tissue is involved in a muscle tear?
A: Muscular tissue – responsible for movement and locomotion.
Q3. What type of tissue is affected in a burn injury on the skin?
A: Epithelial tissue – covers the body, protects against infection, dehydration, and injury.
Q4. Why are tissues specialized in multicellular organisms?
A: To perform specific functions efficiently (division of labour).
Q5. Which connective tissue connects bone to bone and muscle to bone?
A: Ligament connects bone to bone, and Tendon connects muscle to bone.

Case Study: Matter in our surrounding
During summer, Riya kept some ice cubes in a bowl on the table. After a while, she observed that the ice cubes started melting and water droplets formed around the bowl. Later, when the water was heated, it started boiling and steam was produced.
Questions:
Q1. Which process is responsible for the melting of ice cubes?
A: Fusion (Melting) – the change of solid state (ice) into liquid state (water) by absorption of heat.
Q2. Why do water droplets form around the bowl?
A: Due to condensation – water vapour in air loses heat and condenses on the cooler surface of the bowl.
Q3. Which process occurs when water changes into steam?
A: Vaporization (Boiling/Evaporation) – liquid changes into gaseous state on heating.
Q4. Name the phenomenon responsible for the cooling effect during evaporation.
A: Evaporation – particles at the surface gain energy and escape, taking away heat, causing cooling.
Q5. Which factors affect the rate of evaporation?
A : Surface area, temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
Case Study: Is matter arround us pure ?
A group of students performed an experiment to separate a mixture of salt, sand, and water. They first stirred the mixture thoroughly and then filtered it. Sand remained on the filter paper, while the salt solution passed through. Later, they heated the filtrate and obtained salt crystals.
Questions & Answers:
Q1. Which method was used to separate sand from the mixture?
A: Filtration – sand is insoluble and gets separated as residue.
Q2. What was obtained on the filter paper after filtration?
A: Sand (residue) remained on the filter paper.
Q3. Which method was used to obtain salt from the filtrate?
A: Evaporation/Crystallization – salt is left behind after water is removed.
Q4. Why is this mixture considered a heterogeneous mixture?
A: Because the components (sand, salt, water) can be physically separated and are not uniformly distributed.
Q5. Which type of substance is salt – element, compound, or mixture?
A: Compound (sodium + chlorine chemically combined in a fixed ratio).
Q6. Suggest another method (besides evaporation) to obtain pure water from salt solution.
A : Distillation – separates water from dissolved salt based on boiling point difference.
Case Study: Permanent Tissue
A gardener observed that:
- The stem of a tree was very hard and woody.
- The leaves of the plant were green and making food.
- Water and minerals were being transported to the leaves.
- Food was moving from leaves to roots and fruits.
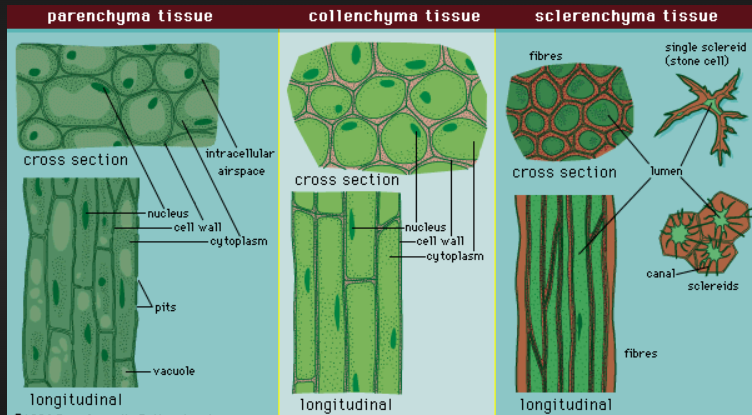
Questions & Answers
- Which permanent tissue makes the stem hard and woody?
A: Sclerenchyma – gives rigidity and mechanical support. - Which permanent tissue in leaves performs photosynthesis?
A: Parenchyma (Chlorenchyma) – contains chloroplasts. - Which permanent tissue transports water and minerals?
A: Xylem. - Which permanent tissue transports food?
A: Phloem. - Why are these tissues called permanent? A: They have lost the ability to divide and are specialize
Half Yearly Science case study 2025
