
Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations – Best Revision Notes PDF (CBSE 2025)
1. Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances (reactants) change to form new substances (products) with different properties.
🔸 2. Chemical Equation
- Word Equation:
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide - Balanced Chemical Equation:
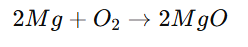
3. Types of Chemical Reactions

- Combination Reaction:
Two or more substances combine to form a single product.
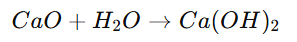
2. Decomposition Reaction:
A single compound breaks into two or more simpler substances.
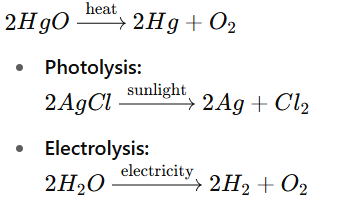
Displacement Reaction:
A more reactive element displaces a less reactive one
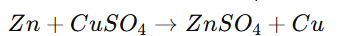
Double Displacement Reaction:
Exchange of ions between two compounds.
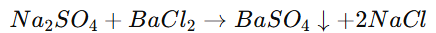
Combustion Reaction:
A substance burns in oxygen to give heat and light
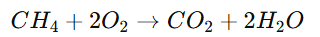
Class 10 Science Chapter 1: Chemical Reactions and Equations – Best Revision Notes PDF (CBSE 2025)
Redox Reaction (Oxidation-Reduction Reaction)

Definition:
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
- Oxidation: Loss of electrons or gain of oxygen.
- Reduction: Gain of electrons or loss of oxygen.
Key Points:
- One substance gets oxidized (loses electrons).
- Another substance gets reduced (gains electrons).
- These processes always happen together.
Example:
Reaction between zinc and copper sulfate: Zn+CuSO4→ZnSO4+Cu
- Zn loses electrons → oxidized
- Cu²⁺ ions gain electrons → reduced
Summary Table:
| Process | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation | Loss of electrons | Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ |
| Reduction | Gain of electrons | Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu |
4. Corrosion
Gradual destruction of metals due to air/moisture.
Example: Rusting of iron
5. Rancidity
Spoiling of food due to oxidation of fats/oils.
Prevention: Airtight containers, refrigeration, antioxidants.
